Sign up to our newsletter !
Recent articles
Tags:
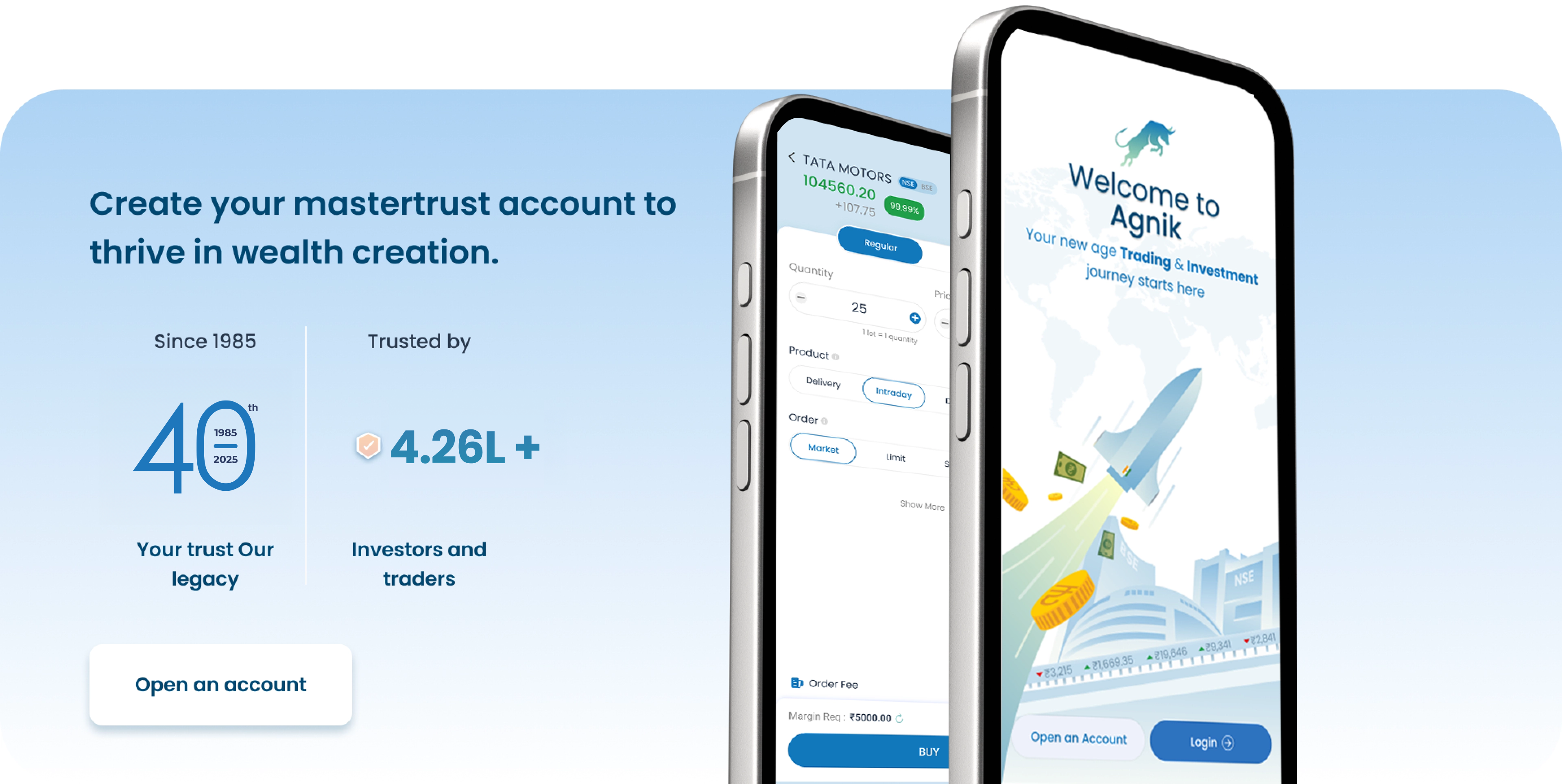
Open a Demat Account in just 15 minutes !

Click on open
account below

Fill out some
basic details

Upload your
documents

Start trading in
24 Hours *
Commonly asked questions
Is Master Capital Services Limited SEBI registered?
Do you have a mobile app for Trading and Finance Management?
What services does mastertrust provide?
What is the minimum investment required to start trading with your company?
Is my personal and financial information secure with your company?
What is your customer support availability?